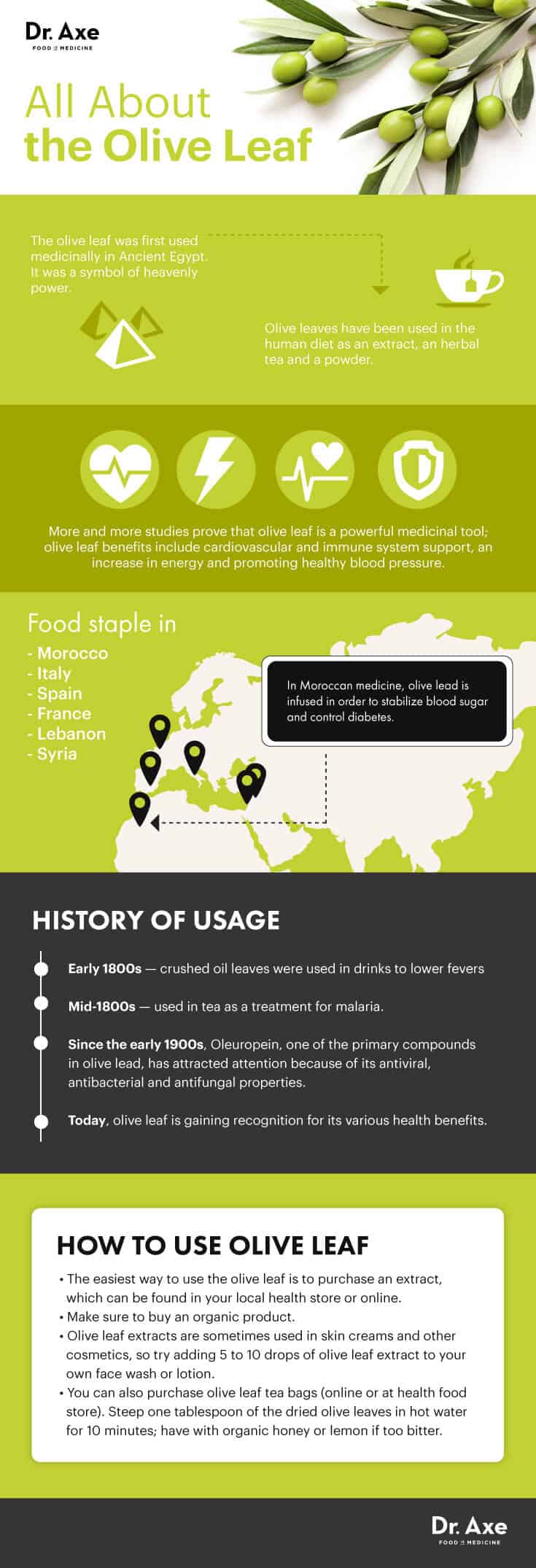
The olive leaf was first used medicinally in Ancient Egypt, and it was a symbol of heavenly power. It is the leaf of the olive tree, called Olea europaea. Olive leaves have been used in the human diet as an extract, an herbal tea and a powder. They contain many potentially bioactive compounds that have antioxidant, antihypertensive, antiatherogenic, anti-inflammatory, hypocholesterolemic and hypoglycemic properties — similar to olive oil benefits.
More and more studies are proving that olive leaf is a powerful medicinal tool; olive leaf benefits include cardiovascular and immune system support, an increase in energy and promoting healthy blood pressure.
In the early 1800s, crushed oil leaves were used in drinks to lower fevers; a few decades later, they were used in tea as a treatment for malaria. In Moroccan medicine, olive lead is infused in order to stabilize blood sugar and control diabetes.
Oleuropein, one of the primary compounds in olive lead, has attracted attention since the early 1900s because of its antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal properties. Studies have found that oleuropein, which is a polyphenol, is a potent antioxidant that lowers blood pressure naturally and prevents cardiovascular disease. Oleuropein proved to be powerful when it made tumors in animals regress or disappear within 12 days.
Olives continue to be a food stable in countries such as Morocco, Italy, Spain, France, Lebanon and Syria, and because of recent scientific studies that prove its health benefits, the olive leaf is becoming increasingly well-known and appreciated outside of olive-growing regions. Today, olive leaf is gaining recognition for its various health benefits.
Olive Tree and Compounds
The olive tree is part of the Oleaceae family, which also includes species such as lilacs, jasmine, Forsythia and the true ash trees. It’s an evergreen tree or shrub that is native to the Mediterranean, Asia and Africa. Typically a short tree that rarely exceeds 26 to 49 feet in height, the flowers are small, white and feathery; the leaves are a silver-green color that grow to be 4 to 10 centimeters long and 1 to 3 centimeters wide.
The olives are harvested in the green-to-purple stage, and they are more fully-fleshed in orchards than in the wild. The seed of the olive is commonly referred to as the pit, and in Britain, it’s called a stone. Researchers believe that the olive tree had its origin approximately 6,000–7,000 years ago in the region corresponding to ancient Persia and Mesopotamia.
One bioactive compound present in olive leaves is the secoiridoid oleuropein, which can constitute up to 6–9 percent of dry matter in the leaves. Other bioactive components found in olive leaves include related secoiridoids, flavonoids and triterpenes; these are plant metabolites that provide health benefits through cell signalling pathways and antioxidant effects.
9 Proven Olive Leaf Benefits
1. Lowers Blood Pressure
A 2011 study evaluated the effectiveness of olive leaf extract in comparison to Captopril, a medication that is given to patients with hypertension or high blood pressure. Five hundred milligrams of olive leaf extract, taken twice daily for eight weeks, significantly reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
While both olive leaf extracts and Captopril were able to prevent high blood pressure levels, the olive leaf treatment also resulted in a reduction of triglyceride levels (reducing bad cholesterol); plus, there are a number of possible side effects when taking Captopril, including dizziness, loss of taste and dry cough.
2. Improves Cardiovascular Health
Olive leaves have been used as an herbal tonic to support cardiovascular function for thousands of years. High doses of olive leaf extract have been shown to help reduce elevated LDL-cholesterol levels and assist in the maintenance of normal blood pressure. Oleuropein, the main glycoside present in olive leaf, and hydroxytyrosol, the principal product of oleuropein that is present in olives and olive leafs, have both been linked to reduction of coronary heart disease and certain cancers.
A study done at the School of Biomedical Sciences in Australia examined rats that were fed a high fat and high carbohydrate diet for 16 weeks. The rats that were not treated developed signs of elevated abdominal and hepatic fat deposition, collagen deposition in heart and liver, cardiac stiffness and oxidative stress markers. The rats that were treated with olive leaf extracts had improved or normalized cardiovascular, hepatic (liver function) and metabolic signs. This study suggests that olive leaf extracts reverse cardiovascular stress and chronic, disease-causing inflammation.
3. Diabetes
One study conducted in Greece measured the effects of olive leaf extracts on the formation of advanced glycation end products (known as AGEs), which are substances that can be a factor in the development of diabetes and many other chronic diseases.Inhibiting AGE formation is a preventive and therapeutic target for patients with diabetes, and a 2013 study found that olive leaf extract did just that, working as a diabetes natural treatment.
Olive leaf extracts have hyperglycemic effects, meaning they reduce blood sugar levels in the body. The olive leaf also controls blood glucose levels in the body. The polyphenols in the olive leaf plays a vital role in delaying the production of sugar, which causes inflammatory diseases like diabetes. One study proved this when olive leaves suppressed the elevation of blood glucose in volunteers after they were consumed starch.
4. Reduces the Risk of Cancer
Olive leaves show an important role as a natural cancer treatment because of its ability to stop the angiogenic process, which stimulates the growth of tumors. The compound oleuropein has an antioxidant and anti-angiogenic effect by inhibiting the reproduction and migration of advanced tumor cells.
A 2009 study conducted in Greece showed, for the first time, that olive leaf extracts have strong antioxidant potency and inhibit cancer and endothelial cell reproduction. Olive leaf extracts slowed the growth of cells associated with breast cancer, urinary bladder cancer and brain cancer.
5. Improves Brain Function
Another olive leaf benefit is its positive effects on brain function. Studies show that oleuropein, one of the main components in olive leaf, reduces the symptoms or occurrence of age-related disorders, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Research suggests that there is a connection between free radicals and Alzheimer’s — because olive leaf is an antioxidant, it helps to combat the damage caused by free radicals and protects the brain from memory loss. Using olive leaf infusions or extracts is a safe and effective way to treat Alzheimer’s disease naturally.
6. Treats Arthritis
Arthritis is a joint disease that causes swelling and pain in the joints; the key word here is swelling — which means inflammation. Because the olive leaf is an anti-inflammatory agent, it works as a natural arthritis remedy.
A 2012 study found that olive leaf extracts significantly reduced paw swelling in rats with arthritis; this is because the extracts were able to reduce the inflammation that was present in the joints. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, impacting more than 33 million American adults. This occurs when the cartilage between the bones and the joint wears down, which allows the bones to rub together rather than giving them the protection and cushion of cartilage.
Studies have shown that olive leaf extracts cuts down on the chronic pain that is associated with osteoarthritis, and it reduces the production of cytokines and enzymes that are markers for the inflammatory process.
7. Kills Bacteria and Fungi
An important olive leaf benefit is its ability to fight off infections, including candida infections, meningitis, pneumonia, chronic fatigue, hepatitis B, malaria, gonorrhea, shingles and tuberculosis; it also naturally treat ear infections, dental and urinary tract infections.
A study done in 2003 proved that olive leave extracts have an antimicrobial effectagainst bacteria and fungi. In the study, the olive leaf extracts killed almost all bacteria tested, including dermatophytes (causing infections on the skin, hair and nails), candida albicans (an agent of oral and genital infections) and Escherichia coli cells (bacteria found in the lower intestine).
8. Improves Immune System
The olive leaf has antiviral properties, giving it the ability to prevent the common cold as well as treat dangerous viruses. Research shows that olive leaf extracts effectively fight against a number of disease-causing microbes, including some of viruses that cause influenza and other respiratory infections.
The powerful compounds found in olive leaves destroy invading organisms and don’t allow viruses to replicate and cause an infection. In fact, the olive leaf is so beneficial to our health that treatment with olive leaf extracts reversed many HIV-1 infection-associated changes in a study done at the New York University School of Medicine.
9. Protects Skin
Olive leaf has the power to reverse years of damage to your skin and the signs of aging. Because of the olive leaf’s antioxidant properties, it helps to prevent certain types of cell damage, especially those caused by oxidation. Foods and herbs that contain antioxidants are great tools for the health of your skin and cells.
The Division of Biochemical Pharmacology in Japan found that olive leaf extract, when given to mice with UV radiation damage, decreased skin thickness and skin elasticity, which are signs of skin damage. The treatment also inhibited skin carcinogenesis and tumor growth.
Some more olive leaf benefits may include:
- more energy
- toothache relief
- diminished food cravings
- joint pain relief
- heartbeat regulation
- improved wound healing
History & Interesting Facts
Several studies have shown that coronary heart disease and cancer rates are the lowest in the Mediterranean area because their diets are rich in olives and olive products.
A 2015 clinical trial published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that the Mediterranean diet, which is high in antioxidant-rich foods, herbs and oils, improves cognitive function. Because oxidative stress and vascular impairment lead to age-related cognitive decline, which is a strong risk factor for the development of dementia, the use of antioxidants in your daily diet makes a major difference.
Of the 334 people who participated in the study, it was the group who followed the Mediterranean diet (consisting of less red meat and more fruits, veggies and whole grains) and took an olive oil supplement (one liter a week) that showed the most improvement after five years.
How to Use Olive Leaf
The easiest way to receive olive leaf benefits is to purchase an extract, which can be found in your local health store or online. Make sure to buy an organic product to assure that it doesn’t include pesticides. Olive leaf extracts are sometimes used in skin creams and other cosmetics, so try adding 5 to 10 drops of olive leaf extract to your own face wash or lotion.
Because of its anti-aging and bacteria-fighting capabilities, you can use olive leaf extract to make a skin-clearing face wash like my Homemade Honey Face Wash. Try adding 5–10 drops of olive leaf extract to my Homemade Body Butter Lotion — it’s completely natural and free of any harmful chemicals. Because of its antibacterial properties, the olive leaf is great for fighting infections in your mouth too, so add five drops of olive leaf extract to this Homemade Remineralizing Toothpaste.
If you have access to an olive tree, then you can use the leaves to make tea. Start by washing the leaves thoroughly, then bake them at about 150 degrees or below until they are dry. Then crush the dry leaves and remove the stalks. Steep one tablespoon of the dried olive leaves in hot water for 10 minutes; drink a cup (or more) a day to get all of these amazing olive leaf benefits. If the taste it too bitter for you, add some organic honey or lemon.
Possible Side Effects & Interactions
Olive leaf is generally safe and doesn’t cause any serious side effects. On occasion, olive leaves may cause dizziness in people who have low blood pressure because it can lower it even further. It may also cause stomach irritations, especially if the dose is too high or the olive leaf tea is too strong. If that happens, dilute the extract with a carrier oil like coconut oil, or add extra water to the tea. Some other side effects may include diarrhea, acid reflux and heartburn.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, do not take olive leaf extract unless it is under the guidance of your physician. There is not enough research to prove that it is safe under these circumstances.
Do not take olive leaf with blood pressure medications since it lowers blood pressure. Olive leaf extract demonstrates hypoglycaemic and antidiabetic properties, so if you are on diabetic medication, start with small doses to ensure that you will not have a reaction. It’s a good idea to speak to your physician beforehand, especially if you have diabetes and are trying olive leaf for the first time.
Olive leaf extract may increase the effect of blood thinners, such as Warfarin. This is because olive leaf may prevent blood platelets from sticking together. If you are taking Warfarin or other blood thinners, check with your physician before taking olive leaf extract.

No comments:
Post a Comment